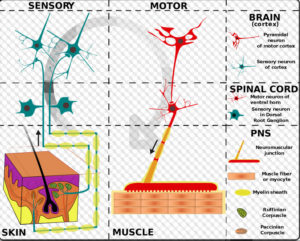
 Today we begin talking some about Nervous system meds – first we’ll talk about the receptors and later this week we’ll go into medications and diseases.
Today we begin talking some about Nervous system meds – first we’ll talk about the receptors and later this week we’ll go into medications and diseases.
Reminder our Nursing School program is live – till the end of August you can get $10 off the monthly price. Details can be found here – http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/nursing-school-nclex-prep-course/
A review of our other NCLEX drug posts in the series are linked at the bottom of this article.
Muscarinic agonists (parasympathomimetic à Bethanechol
Muscarinic antagonists–> Atropine
Ganglionic-stimulating agents –> Nicotine
Cholinesterase inhibitors (ChE) –> Physostigmine or neostigmine
Neuromuscular-blocking agents –> Tubocurarine
Adrenergic agonists (sympathomimetic) –> Epinephrine
Adrenergic antagonists block α & β receptors
Prazosin α adrenergic antagonist
Propanolol β adrenergic antagonist
Receptors –
NicotinicN
- Release of epinephrine from adrenal medulla
NicotinicM
- Located at neuromuscular junction of skeletal muscle
- Causes skeletal muscle contraction
Muscarinic Receptors
- Decreased secretions from lungs, stomach, intestines, sweat glands
- Decrease in HR
- Smooth muscle contraction in bronchi and GI tract
- Miosis (sphincter contraction) and accommodation (ciliary contraction)
- Voiding due to contraction of detrusor muscle and relaxation of trigone and sphincter muscles
Alpha1
- Mydriasis d/t radial muscle contraction
- Veins and arterioles are activated to constrict
- Increased peripheral resistance, Increased blood pressure
- Male sex organs are activated to promote ejaculation
- Contraction of prostatic capsule, trigone, and sphincter muscles
Dopamine
- Dilates blood vessels in the kidneys
Beta1
- Predominant receptor found on the heart
- Increased HR, Increased Contraction Force, Increased Conduction through AV node
- Increased lipolysis
- Release of Renin by the kidneys
Beta2
- Dilates bronchi
- Relaxes uterine smooth muscle
- Vasodilation of arterioles in heart, lungs, and skeletal muscle
- Slightly decreased peripheral resistance
- Increased glycogenolysis in the liver and muscles
- Skeletal muscle contraction
Our other NCLEX Medication articles
http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/nclex-test-help-pain-meds-and-inflammation/
http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/nclex-drugs-immunity-and-chemotherapy/
http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/anti-infective-drugs-part-1/
http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/drug-categories-for-nclex-part-1-of-2/
http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/nclex-drug-categories-part-2/


No Responses