 We continue our series on Cardiac Drugs – you can find part one of the series here – http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/cardiac-drugs-for-nclex-part-1/
We continue our series on Cardiac Drugs – you can find part one of the series here – http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/cardiac-drugs-for-nclex-part-1/
Centrally Acting α2 Agonists
Expected Action:
Decreased sympathetic outflow in CNS – > bradycardia, Decreased CO, vasodilation, Decreased BP
Example: clonidine (Catapres) –
Others: guanfacine (Tenex), methyldopa (Aldomet)
Therapeutic Uses:
Hypertension, Severe cancer pain (epidural), Investigational: Migraine, flushing from menopause, withdrawal management
Adverse Effects:
Dry mouth (usually resolves in 2-4 weeks)
Drowsiness & sedation
Rebound hypertension
Contraindications/Precautions:
Pregnancy (C)
Interactions:
Antihypertensives: Additive hypotensive effect
Prazosin, MAOIs, TCAs: Counteract effects of clonidine.
CNS Depressants: Additive CNS depressant effect
Education:
Apply patch to hairless skin on torso or upper arm
β-Adrenergic Blockers
Expected Action:
β1-adrenergic blockade Decreased HR, Decreased contractility, Decreased AV conduction
Examples: Cardioselective: metoprolol (Lopressor), Nonselective: propanolol (Inderal) – Others: Cardioselective: atenolol, Nonselective: nadolol (Corgard)
Therapeutic Uses:
Hypertension, Dysrhythmias (block SA/AV cond.), Angina/MI (Decreased O2 demand – increased diastole time \ increased perfusion – Decreased BP leads to Decreased O2), Heart failure (mechanism unknown, probably related to above), Hyperthyroidism, migraines, stage fright, pheochromocytoma, glaucoma
Adverse Effects:
- β1 – Bradycardia, Decreased CO, AV block, Orthostatic hypotension, Rebound myocardium excitation (d/c over 1-2 weeks)
β2 – Bronchoconstriction, Glycogenolysis inhibited
Contraindications/Precautions:
CI: AV block, sinus bradycardia
Nonselectives are CI ĉ asthma, bronchospasms, heart failure
Interactions:
β1: calcium-channel blockers verapamil (Calan) and diltiazem (Cardizem) intensify effects of β-blockers.
β2: Insulin – prevents glycogenolysis
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors
Expected Action:
Block production of angiotensin II leads to arteriole vasodilation, excretion of Na+ and H2O, retention of K+, and possible pathological changes to vessels and heart
Proto: captopril (Capoten) — Others: enalapril (Vasotec), fosinopril (Monopril), lisinopril (Prinivil), ramipril (Altace
Therapeutic Uses:
Heart failure, Hypertension, MI (Decreased risk of HF and mortality), Peripheral neuropathy, Ramipril can prevent MI, stroke, or death in high-risk patients
Adverse Effects:
Hyperkalemia, Cough, Neutropenia, Angioedema (swelling in tongue/oropharynx) – treat with epinephrine, First-dose orthostatic hypotension, Rash & dysgeusia
Contraindications/Precautions:
Pregnancy (D)
CI: bilateral renal stenosis, history of angioedema
Interactions:
Diuretics leads to 1st-dose hypotension
Lithium leads to increased [Lithium]
Antihypertensives leads to Additive effects
NSAIDs Decreased antihypertensive eff
- K+ supplements/K+ sparing diuretics leads to hyperkalemia
Education:
Captopril 1 hr ac / others ĉ or ŝ food
Should see increased renal function evidenced by Decreased proteinuria
Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs)
Expected Action:
- Blocks action of angiotensin leads to arteriole vasodilation, excretion of Na+ & H2O, retention of K+
Δ ACE and ARB is that cough and hyperkalemia are not side effects of ARB.
Proto: Losartan (Cozaar) — Others: valsartan (Diovan), irbesartan (Avapro), candesartan (Atacand), olmesartan (Benicar)
Therapeutic Uses:
Decreased hypertension (all)
Stroke prevention (losartan)
Mgt of heart failure / mortality prevention after MI (valsartan)
Delay progression of diabetic neuropathy (irbesartan, losartan)
Adverse Effects:
Angioedema
Fetal injury
Contraindications/Precautions:
Pregnancy (D)
CI: Renal stenosis
Caution ĉ Hx of angioedema
Education:
ARBs can be taken with or without food
Should see increased renal function evidenced by Decreased proteinuria
Calcium Channel Blockers
Expected Action:
Nifedipine: V vascular Ca2+channels leads to vasodilation peripheral & heart arterioles
Verapamil, Diltiazem: Above + Decreased contractility, Decreased HR, Decreased AV conduction
Examples: nifedipine (Adalat) — Others: amlodipine (Norvasc), felodipine (Plendil), nicardipine (Cardene), verapamil (Calan), diltiazem (Cardizem)
Therapeutic Uses:
All: Hypertension, All but Felodipine: Angina, Verapamil, Diltiazem: Hypertension, Angina, Dysrhythmias
Adverse Effects:
Nifedipine: Tachycardia, peripheral edema, acute toxicity
Verapamil, Diltiazem: Orthostatic hypotension, peripheral edema, constipation, cardiac suppression, dysrhythmias, acute toxicity
Contraindications/Precautions:
CI: heart block, hypotension, bradycardia, aortic stenosis, severe heart failure
Interactions:
Verapamil, Diltiazem
Grapefruit leads to toxicity, Digoxin leads to increased [digoxin], β-blockers: leads to HF, AV block, bradycardia
Nifedipine:
Grapefruit leads to toxicity, β-blockers: Used to Decreased reflex tachycardia
Education:
Administer IV over 2-3 minutes
Meds for Hypertensive Crisis
Expected Action:
Direct vasodilation of veins and arteries causing rapid Decreased BP (preload/afterload)
Proto: nitroprusside — Others: labetalol (Trandate), diazoxide (Hyperstat), fenoldopam (Corlopam), trimethaphan (Arfonad)
Therapeutic Uses:
Hypertensive emergencies, Decreased bleeding during surgery by producing controlled hypotension
Adverse Effects:
Excessive hypotension
Cyanide poisoning: increased risk ĉ liver dysfunction; Give slowly (5 mcg/kg/min) along with thiosulfate to deactivate cyanide.
Thiocyanate poisoning: Can manifest as altered mental state/psychosis. Avoid prolonged use (>3 d). Plasma thiocyanate should be <0.1 mg/mL
Contraindications/Precautions:
Pregnancy (C)
Education:
Discard solutions that are blue, red, or green
Protect solutions from light
Do not mix other meds ĉ nitroprusside.
Organic Nitrates
Expected Action:
- ò cardiac O2 demand by dilating veins and decreasing venous return (preload)
Relaxes or prevents spasms in coronary arteries thus increased O2 supply
Proto: nitroglycerine — Others: isosorbide dinitrate (Imdur)
Therapeutic Uses:
Treatment of angina (acute, variant, and prophylaxis)
IV perioperative BP control, HF d/t acute MI
Adverse Effects:
Headache, Tolerance, Orthostatic hypotension, Reflex tachycardia – give metoprolol (Lopressor)
Contraindications/Precautions:
CI: traumatic head injury leads to increased ICP
Interactions:
Sildenafil (Viagra) leads to Acute or fatal hypotension
EtOH, β-blockers, Ca-blockers, diuretics – additive hypotensive effects
Education:
Sublingual tab/translingual spray: R onset, S duration
Transmucosal: R onset, L duration
SR caps: S onset, L duration
Transdermal: S onset, L duration (hairless area, min 8 hr/day without med to lower risk of developing tolerance.
Topical: S onset, L duration
IV: Use glass bottle & mfr’s tubing; Start at slow rate (5 mcg/min)
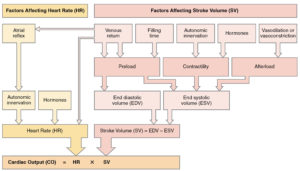
Cardiac Glycosides
Expected Action:
(+) inotropic leads to increased SV, CO
(-) chronotropic leads to > fill time leads to increased SV, CO
Proto: digoxin
Adverse Effects:
GI effects, CNS effects (fatigue, vision changes), Dysrhythmias, cardiotoxicity: increased risk from leads to decreased K+, Decreased [digoxin], heart disease
Contraindications/Precautions:
CI: v-fib, v-tach, 2/3º blocks
Interactions:
Quinidine leads to increased dig toxicity
Verapamil leads to increased [digoxin]
Sympathomimetics add to inotropic effect
Loop & thiazide diuretics leads to Decreased K+ leads to increased risk of digoxin dysrhythmia
ACE inhibitors / ARBs leads to increased risk increased K+ leads to ò therapeutic digoxin effects
Education:
Check apical pulse: hold < 60 (adults), < 70 (kids), < 90 (infants)
Therapeutic levels = 0.5-2 ng/mL
Treat bradycardia ĉ atropine
Treat dysrhythmias ĉ phenytoin or lidocaine
Activated charcoal or cholestyramine can bind digoxin to prevent absorption.
Antidysrhythmics
(Class IA: Na+-Channel Blockers)
Expected Action:
Decreased conduction / increased automaticity / Decreased repolarization rate
Sodium channel blockers: procainamide (Pronestyl), quinidine, disopyramide, tocainide, propafenone
Therapeutic Uses:
Supraventricular tachycardia, Ventricular tachycardia, Atrial fibrillation
Adverse Effects:
Systemic lupus syndrome (resolve with d/c medication)
Blood dyscrasias
Cardiotoxicity (increased QRS, increased QT)
Contraindications/Precautions:
CI: Sens. to quinidine, complete ♥ block, lupus
Interactions:
Antihypertensives leads to additive hypotensive effect
Anticholinergics leads to increased anticholinergic effects
Antidysrhythmics leads to increased in therapeutic effects / increased toxicity potential
Past Medication posts –
Nervous System Meds (4 parts)
http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/nervous-system-medication-part-1-the-receptors/
http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/nervous-system-meds-drugs-part-2/
http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/medications-affecting-the-nervous-system-part-3/
Pain Meds and Inflammation – http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/nclex-test-help-pain-meds-and-inflammation/
Immunity and Chemo – http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/nclex-drugs-immunity-and-chemotherapy/
Anti Infective Drugs – http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/anti-infective-drugs-part-1/
More information can be found on our blog – http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/the-blog/



