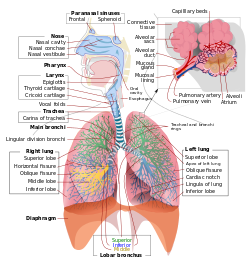
Respiratory System NCLEX Medications
Key points –
Bronchodilators An overview
- β2-adrenergic agonists
- Inhaled, short-acting – Albuterol (Proventil, Ventolin)
- Inhaled, long-acting Formoterol, salmeterol
Oral, long-acting Albuterol, terbutaline
Methylxanthines
- Oral, long-acting – heophylline
Anti-cholinergics
- Maintenance therapy – Ipratropium, inhaled (Atrovent)
Bronchodilators are oral or inhaled, for acute relief, short-term prophylaxis and long-term control. Anti-inflammatory are for long-acting prophylaxis.
Anti-inflammatory
Glucocorticoids
- Inhaled medications
Beclomethasone (QVAR)
Budesonide (Pulmicort)
Fluticasone (Flovent)
Triamcinolone (Azmacort) - Oral medications – Prednisone, prednisolone
- Cromolyn & nedocromil (inhaled)
- Leukotriene modifiers (Oral)
- Montelukast (Singulair)
- Zafirlukast (Accolate)
β2-Adrenergic Agonists
Expected Action:
Selectively activate β2 receptors resulting in bronchodilation: bronchospasm is relieved, histamine release is inhibited, and ciliary motility is increased.
Example: albuterol (Proventil) — Others: formoterol (Foradil), salmeterol (Serevent),terbutaline (Brethine)
Therapeutic Uses:
Albuterol: Inhaled, short-acting and oral, long-acting
Formoterol, salmeterol: Inhaled, long-acting
Terbutaline: Oral, L-A
Adverse Effects: Inhaled: Minimal adverse effects, Oral: Tachycardia/angina d/t β1 in ♥/ tremors d/t β2 in skeletal muscle
Contraindications/Precautions: Pregnancy (C), CI: tachydysrhythmias
Interactions:
β-blockers like propanolol leads to negate effects of both
TCAs and MAOIs leads to increased risk of tachycardia and angina
Education:
Inhale 3-5 sec, hold 10 sec, wait 60 sec for next dose
Use inhaled β2-agonist before using inhaled glucocorticoid
Methylxanthines – Theophylline (Theolair)
Expected Action:
Theophylline relaxes bronchial smooth muscle leads to bronchodilation
Therapeutic Uses: Long-term control of asthma
Adverse Effects:
Mild toxicity leads to GI distress & restlessness. Severe reactions
Severe reactions can occur at ñ therapeutic levels and include dysrhythmias and seizures. Effects unlikely @ <20 mcg/mL. Activated charcoal ò absorption, lidocaine for dysrhythmias and diazepam for seizures.
Contraindications/Precautions: Pregnancy (C)
Interactions:
Caffeine: increased CNS/♥ effects of theophylline. Also increased [theophylline]
Phenobarbital, phenytoin: decrease [theophylline]
Cimetidine, ciprofloxacin: increase [theophylline]
Inhaled Anticholinergics
Expected Action:
Block muscarinic receptors on bronchi leads to bronchodilation
Example: ipratropium (Atrovent) — Others: tiotropium (Spiriva)
Therapeutic Uses:
Relief of bronchospasms associated with COPD
Relief of allergen-induced and exercise-induced asthma.
Adverse Effects:
Local anticholinergic effects
Contraindications/Precautions: Pregnancy (B), CI: Peanut allergy, Caution in narrow-angle glaucoma
Education:
Usual adult dose is 2 puffs (1 minute apart)
If taking two inhaled medications, separate by at least 5 minutes.
Glucocorticoids
Expected Action:
Prevent inflammation, suppress airway mucous production, and promote responsiveness of β2-receptors in bronchial tree.
Example: beclomethasone (QVAR) — Others: budesonide (Pulmicort), fluticasone (Flovent), triamcinolone (Azmacort), prednisone (Deltasone)
Therapeutic Uses: Inhaled: Long-term asthma prophylaxis, S-T, oral: Treat symptoms following acute asthma., L-T, oral: Treat chronic asthma, 1º adrenocortical insufficiency, Promote lung maturity and decreased RDS in fetuses at risk for preterm birth.
Adverse Effects:
Inhaled: Dysphasia, candidiasis, bone loss
Oral (≥10d): decreased adrenal gland function / bone loss / hyperglycemia / glucosuria / / infection / peptic ulcer disease / myopathy / fluid & electrolyte disturbances.
Contraindications/Precautions: Pregnancy (?), CI: Live virus / systemic fungal infect.
Interactions: Diuretics: ñ hypokalemia, NSAIDs: ñ GI ulceration, Glucocorticoids counteract effects of insulin and oral hypoglycemics.
Education:
Oral are for short-term use, 3-10 days following acute attack
Mast Cell Stabilizers
Expected Action:
- Anti-inflammatory: Stabilize mast cells, inhibiting histamine release.
Suppress inflammatory cells (e.g. eosinophils, macrophages)
Examples: Cromolyn (Intal) — Others: nedocromil (Tilade)
Therapeutic Uses:
Management of chronic asthma, Prophylaxis of exercise-induced and allergen-induced asthma attacks, Allergic rhinitis by intranasal route
Adverse Effects: Safest of all asthma meds / safe for kids
Contraindications/Precautions: Pregnancy (B), Propellant CI: CAD, dysrhythmias, and status asthmaticus
Leukotriene Modifiers
Expected Action:
Prevent effects of leukotrienes thus suppressing inflammation, airway edema, bronchoconstriction, and mucus production.
Examples: montelukast (Singulair) — Others: zileuton (Zyflo), zafirlukast (Accolate)
Therapeutic Uses: Long-term asthma therapy in folks ≥ 12 YO
Adverse Effects: Liver injury ĉ zileuton and zafirlukast. (nausea, anorexia, abdominal pain)
Contraindications/Precautions: Pregnancy (?)
Interactions:
Zileuton / zafirlukast inhibit warfarin metabolism leads to increase [warfarin]
Zileuton / zafirlukast inhibit theophylline metabolism leads to increase theophylline toxicity
Education:
Zileuton given without regard to food. Zafirlukast taken ŝ food
Antitussive – Opioids
Expected Action:
Suppresses cough center in the medulla oblongata.
Example : codeine — Others: hydrocodone
Therapeutic Uses: Chronic, non-productive cough
Adverse Effects:
GI distress (nausea, constipation) – take ĉ food, leads to fluid/fiber, CNS sedation effects: Respiratory depression (<12/min) – naloxone, Potential for abuse, schedule II.
Contraindications/Precautions: Pregnancy (C), CI: acute asthma, head trauma, liver/renal dysfunction, acute alcoholism
Mucolytics
Expected Action:
Enhance flow of secretions in the respiratory passages
Example: acetylcysteine (Mucomyst) — Others: hypertonic saline
Therapeutic Uses: Acute & chronic pulmonary disease ĉ increase secretions, Cystic fibrosis, Acetylcysteine is the antidote for acetaminophen poisoning
Adverse Effects: Aspiration and bronchospasm
Contraindications/Precautions: Pregnancy (B), CI: GI bleeding, Caution: Peptic ulcers / esophageal varices / severe liver disease
Education:
Has smell of rotten eggs, Dilute in fruit juice, IV: Loading dose, next dose over 4h, last dose over 16h.
Decongestants
Expected Action:
Stimulate α1-adrenergic receptors leads to decreased inflammation of nasal membranes
Example: Phenylephrine Others: Ephedrine, naphazoline, phenylpropanolamine
Therapeutic Uses: Allergic rhinitis, sinusitis, and common cold
Adverse Effects: Rebound congestion (Max 3-5 days, taper down use), CNS stimulation (rare ĉ topical), Vasoconstriction
Contraindications/Precautions: Pregnancy (?), CI: Chronic rhinitis, Caution: CAD and hypertension
Education: Oral do not lead to rebound congestion
Past Medication posts –
Nervous System Meds (4 parts)
http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/nervous-system-medication-part-1-the-receptors/
http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/nervous-system-meds-drugs-part-2/
http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/medications-affecting-the-nervous-system-part-3/
Cardiac Medications
Part 1 – http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/cardiac-drugs-for-nclex-part-1/
Part 2 – http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/nclex-cardiac-drugs-part-2/
Part 3- http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/nclex-cardiac-drugs-part-3/
Pain Meds and Inflammation – http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/nclex-test-help-pain-meds-and-inflammation/
Immunity and Chemo – http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/nclex-drugs-immunity-and-chemotherapy/
Anti Infective Drugs – http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/anti-infective-drugs-part-1/
More information can be found on our blog – http://www.nclexreviewonline.com/the-blog/